SpaceX has completed its 40th Falcon 9 launch of 2022, delivering a new batch of Starlink satellites and Boeing demonstration satellite into orbit.
Right on schedule, Falcon 9 lifted off from SpaceX’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) LC-40 pad at 10:09 pm EDT, Sunday, September 4th. The rocket’s reused booster and fairing and new upper stage performed as expected, continuing Falcon 9’s unprecedented streak of 149 successful launches. Flying for the seventh time overall, former Falcon Heavy booster B1052 performed flawlessly after a quick 31-day turnaround and touched down on SpaceX drone ship Just Read The Instructions’ (JRTI) deck several hundred miles downrange less than nine minutes after liftoff.
Flying for the fourth and fifth times, the Starlink 4-20 mission’s Falcon 9 fairing halves also worked as expected on ascent. SpaceX does not discuss fairing recovery but both halves likely deployed parafoils after reenter Earth’s atmosphere and gently splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean. SpaceX support ship Doug will eventually fish them out of the water for reuse.
Not merely a Starlink mission, Starlink 4-20 was SpaceX’s sixth Starlink rideshare. Sitting atop the stack of 51 Starlink V1.5 satellites was an experimental spacecraft built by Spaceflight Inc. Known as Sherpa-LTC2, Spaceflight and partner Astro Digital turned the orbital transfer vehicle (space tug) into a satellite for customer Boeing. The purpose: carry and test a prototype communications payload built by Astro Digital and designed to verify new V-band communications technologies for a planned constellation of Boeing satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approved Boeing’s plans for a 147-satellite V-band constellation in November 2021. It’s unclear what the purpose of the constellation would be or if Boeing already has customers or partners lined up. The prototype spacecraft built by Spaceflight and Astro Digital – known as Varuna in recent FCC filings – will be crucial for determining the constellation’s future. Boeing wants to use a swath of spectrum known as the V-band that has a higher frequency than the Ku and Ka bands commonly used by most other communications satellites. A higher frequency could mean higher connection speeds and more available bandwidth, but V-band radio waves tend to struggle to pierce through rain and other adverse weather conditions.
Varuna should help Boeing fully determine whether that interference is a showstopper or something that can be managed. Boeing applied for an FCC license for its V-band constellation in 2017. It’s unclear whether a lack of interest on Boeing’s part or problems with the application caused the process to take as long as it did.
Varuna was successfully deployed from Falcon 9 a bit less than 50 minutes later in a mostly circular orbit 316 kilometers (196 mi) above Earth’s surface. Outfitted with a propulsion system designed by startup Benchmark Space, Sherpa-LTC2 is meant to eventually raise itself into an operational orbit around 1050 kilometers (~650 mi), where the V-band payload can be tested at the same altitude as Boeing’s planned constellation.
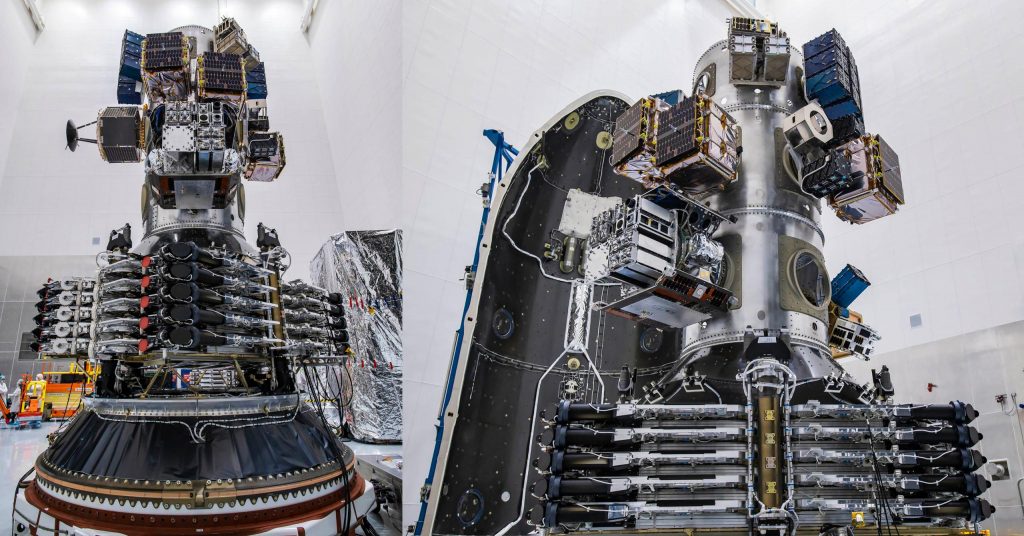
20 minutes after Varuna’s deployment, Falcon 9’s upper stage – spinning end over end – released all 51 Starlink satellites at once, completing the payload portion of the mission. As always, the upper stage will likely perform a deorbit burn within a few hours of liftoff and should reenter Earth’s atmosphere not long after, ensuring that the only space debris produced by the mission is the Varuna deployment mechanism and a set of four benign Starlink ‘tensioning rods’ that should reenter in about two months.
Starlink 4-20 was SpaceX’s 40th launch of 2022 and 50th launch in 12 months. According to Next Spaceflight, the company has plans for at least two more Starlink launches within the next eight days. Starlink 4-2, another rideshare mission, is scheduled no earlier than September 10th, while Starlink 4-34 could launch on September 12th.



ivermectin 12 mg tablet – purchase atacand sale where to buy tegretol without a prescription
buy isotretinoin 10mg sale – buy linezolid 600 mg generic buy zyvox medication
purchase azithromycin for sale – tinidazole online buy nebivolol 5mg over the counter
vibra-tabs sale – order glipizide pills glucotrol pill
purchase augmentin online cheap – cymbalta canada order duloxetine pills
viagra overnight delivery – brand cialis how much is cialis
generic omeprazole 10mg – buy omeprazole 20mg online cheap atenolol 50mg sale
medrol 8 mg oral – triamcinolone 10mg oral triamcinolone pill
buy acyclovir 800mg without prescription – buy rosuvastatin 10mg online cost crestor 10mg